
The Role of Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes

Chronic inflammation can contribute to the development and progression of a number of diseases, including type 2 diabetes. In this article, we will explore the link between inflammation and type 2 diabetes, including the underlying mechanisms, risk factors, and treatment options. By understanding this link, we can better prevent and manage this increasingly prevalent condition.
Chronic inflammation and insulin resistance: How do they relate?
Chronic inflammation and insulin resistance are closely related and can contribute to the development and progression of type 2 diabetes.
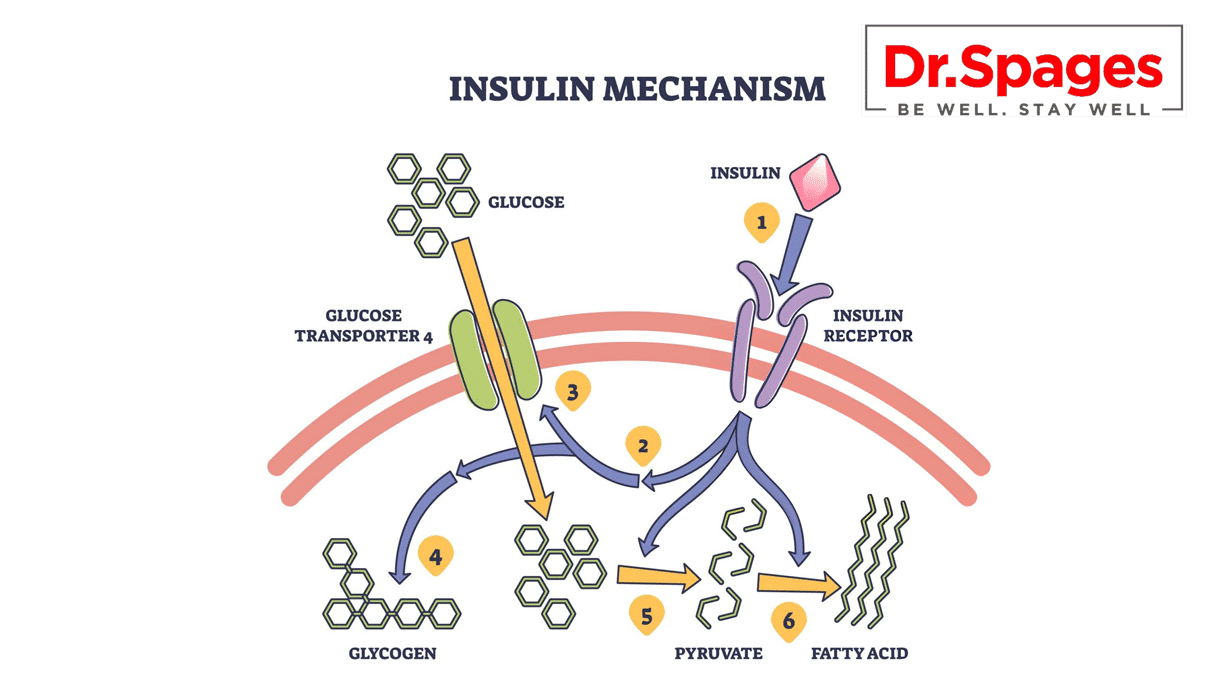
Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated levels of glucose in the blood. Chronic inflammation can contribute to insulin resistance by promoting the release of cytokines and other inflammatory molecules that interfere with insulin signaling pathways.
These cytokines can cause the death of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to decreased insulin production and further exacerbating insulin resistance. Additionally, chronic inflammation can contribute to the accumulation of fat in the liver and other tissues, which can further impair insulin sensitivity.
Several risk factors can contribute to chronic inflammation, including a diet high in saturated and trans fats, smoking, stress, and physical inactivity. By addressing these risk factors, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic inflammation and, in turn, decrease their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Treatment options for chronic inflammation and insulin resistance include lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, stress reduction techniques, and smoking cessation. In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. However, lifestyle modifications should always be the first line of defense in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes.
Underlying mechanisms: What causes chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetes?
Chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetes is a complex and multifactorial process that involves several underlying mechanisms. Here are some of the main causes of chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetes:
Adipose tissue dysfunction
Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism and immune response. In individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes, adipose tissue becomes dysfunctional and releases pro-inflammatory cytokines that contribute to chronic inflammation.
Oxidative stress
Oxidative stress is an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to detoxify them. ROS can cause damage to cells, tissues, and organs, leading to inflammation and insulin resistance.
Gut microbiota
The gut microbiota, which is the collection of microorganisms that reside in the gastrointestinal tract, plays a crucial role in regulating immune function and metabolism. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut microbiota composition, has been associated with chronic inflammation and type 2 diabetes.
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs)
Sugars react with proteins and lipids in the body to produce AGEs. Tissue accumulation of AGEs is associated with inflammation and insulin resistance in people with type 2 diabetes.
Immune dysfunction
The immune system plays a crucial role in regulating inflammation and protecting the body from infection. In individuals with type 2 diabetes, immune dysfunction can contribute to chronic inflammation and insulin resistance.
By addressing these underlying mechanisms, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic inflammation and, in turn, decrease their risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Treatment options include lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and smoking cessation, as well as medication to manage inflammation and insulin resistance in severe cases.
Potential Complications of Chronic Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes
Chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetes can lead to several complications that can affect various organs and systems in the body. Some of the potential complications of chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetes are:
Cardiovascular disease
Atherosclerosis, which may cause heart attack and stroke, develops when blood arteries are damaged by chronic inflammation.
Diabetic retinopathy
Inflammation can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can cause vision loss.
Diabetic nephropathy
Chronic inflammation can cause damage to the small blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to diabetic nephropathy, a condition that can cause kidney failure.
Diabetic neuropathy
Inflammation can cause damage to the nerves, leading to diabetic neuropathy, a condition that can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the extremities.
Foot ulcers
Inflammation can cause poor blood flow to the feet, leading to the development of foot ulcers, which can become infected and may require amputation in severe cases.
Increased risk of infections
Chronic inflammation can weaken the immune system, making individuals with type 2 diabetes more susceptible to infections.
Mental health issues
Inflammation has been linked to depression and anxiety, which are more common in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
It is essential to manage chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetes to prevent these complications and improve overall health outcomes.
Treatment options
Lifestyle changes and other approaches can be effective in reducing inflammation and managing type 2 diabetes. Here are some treatment options:
Lifestyle changes
One of the most effective ways to reduce inflammation and manage type 2 diabetes is through lifestyle changes. These include a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and smoking cessation. A healthy diet that is low in processed foods, added sugars, and saturated fats can help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. Exercise can also help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation. Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help reduce inflammation by lowering stress hormones in the body.
Supplements
Certain supplements may help reduce inflammation in individuals with type 2 diabetes. These include omega-3 fatty acids, which are found in fish oil, and curcumin, which is found in turmeric. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity, while curcumin has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects.
Discover the power of natural supplements in combating inflammation and improving your overall health, with our carefully selected range available at drspages
It is important to note that treatment options should be tailored to the individual and used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. A combination of lifestyle changes and medications may be necessary to effectively manage inflammation and type 2 diabetes.
Inflammatory Biomarkers as Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes Progression and Response to Treatment
Inflammatory biomarkers are molecules produced by the body in response to inflammation. These biomarkers are widely used in research to study the progression of type 2 diabetes and its response to treatment. Inflammation is a critical factor in the development of type 2 diabetes and its complications, including cardiovascular disease, retinopathy, and neuropathy. By measuring inflammatory biomarkers, researchers can predict the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes and the response to various treatments.
C-reactive protein (CRP) is one of the most widely studied inflammatory biomarkers in type 2 diabetes. CRP is a protein produced in the liver in response to inflammation. Studies have shown that elevated CRP levels are associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes and its complications.
Another inflammatory biomarker that has been studied in type 2 diabetes is interleukin-6 (IL-6). IL-6 is a cytokine that is involved in the regulation of the immune system and inflammation. Elevated levels of IL-6 have been linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease. Studies have also shown that IL-6 levels can predict the response to certain treatments, including thiazolidinediones and GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) is another inflammatory biomarker that has been studied in type 2 diabetes. TNF-α is a cytokine that is involved in inflammation and insulin resistance. Elevated levels of TNF-α have been linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes and its complications, including cardiovascular disease and kidney disease. Studies have also shown that TNF-α levels can predict the response to certain treatments, including insulin sensitizers and GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Conclusion
Inflammation plays a significant role in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes, and reducing inflammation can be an effective way to manage the condition. Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and smoking cessation, can help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. Medications, and supplements, may also be effective in reducing inflammation and managing type 2 diabetes. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses both inflammation and other factors that contribute to type 2 diabetes. By managing inflammation, individuals with type 2 diabetes can improve their overall health and reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition.












Thanks for this article. There’s so much to learn, but it’s all good.
You are welcome!!