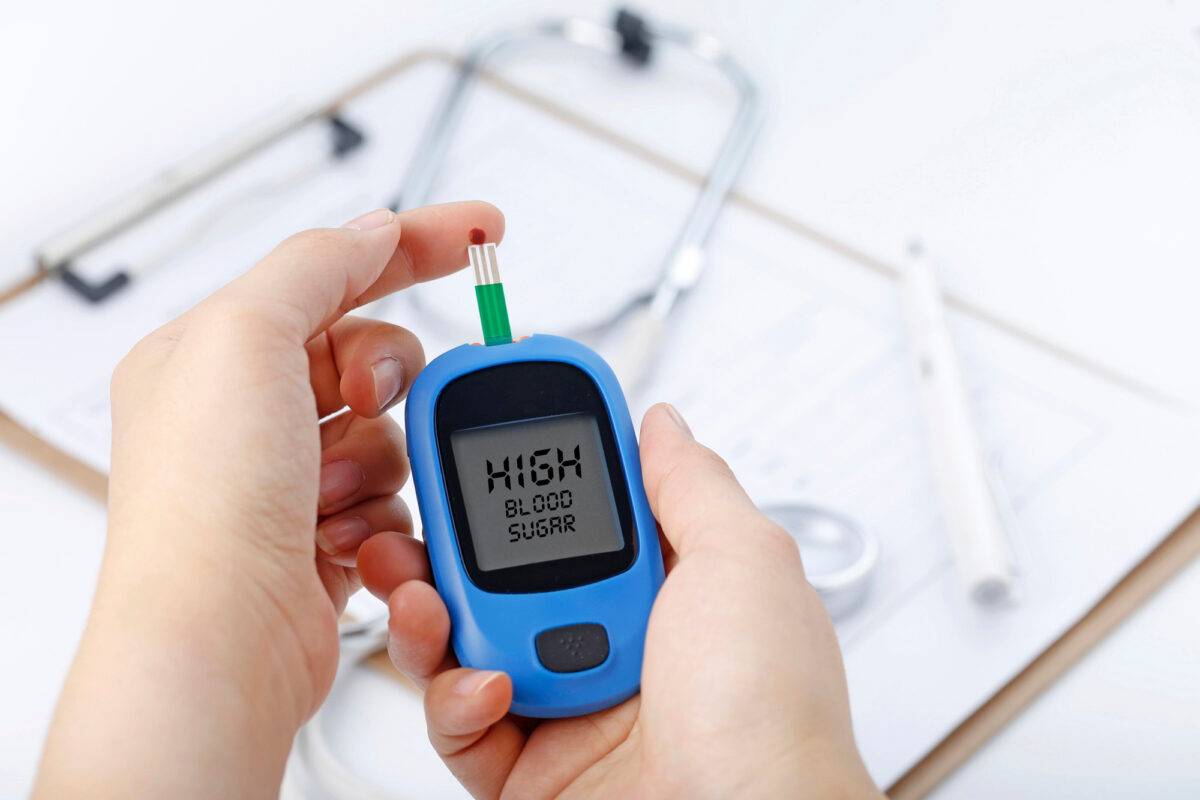
High Blood Sugar Despite No Dietary Sugar
High Blood Sugar Despite No Dietary Sugar
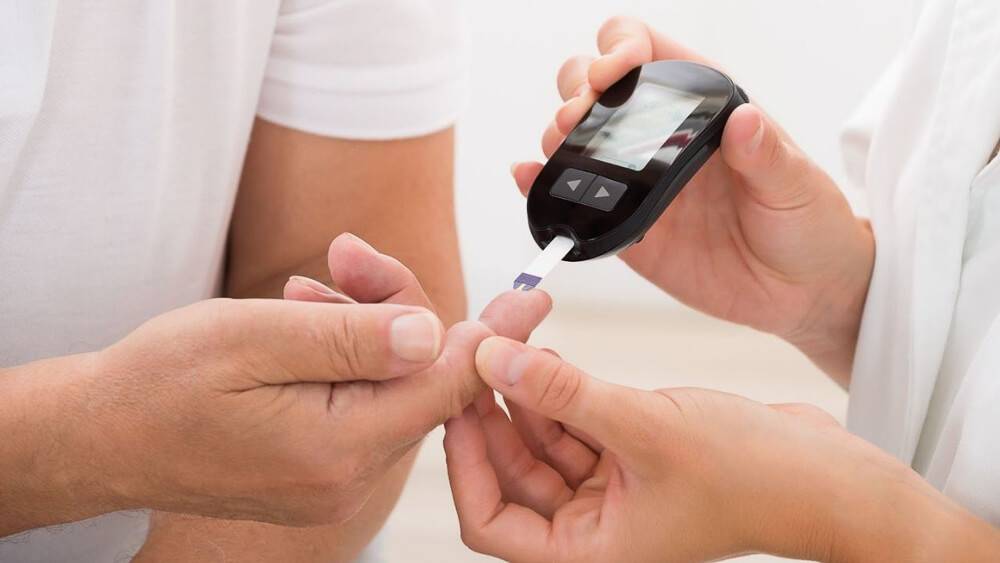
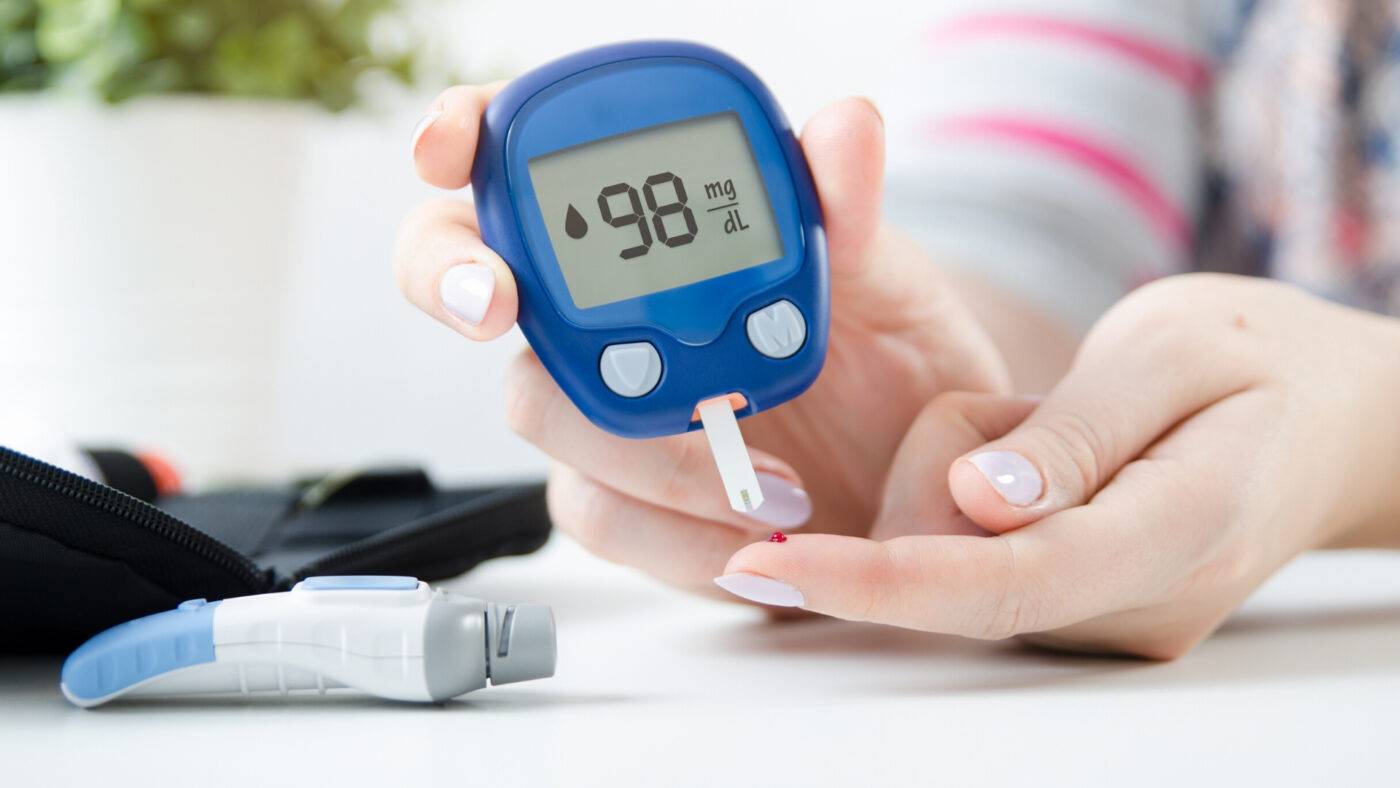
High blood sugar levels while not eating sugar might be perplexing and alarming. However, it is critical to recognize that blood sugar management is a complex process that is influenced by a variety of factors such as dietary choices, physical activity, medication, stress, and underlying health issues.
Healthy Recipes Cookbook by Dr Spages
Welcome to Dr. Jonathan Spages’ Healthy Recipes Cookbook, a culinary treasure trove filled with delectable and health-conscious recipes catering to various dietary needs, including Paleo, Gluten-Free, and Grain-Free options. This cookbook offers instant download access, allowing users to conveniently explore and prepare these nutritious dishes on their mobile devices or computers. The cookbook is designed to be easily accessible and user-friendly, ensuring a seamless cooking experience. Don’t miss out on this exclusive online-only offer – embark on a journey to a healthier lifestyle with Dr. Spages’ Healthy Recipes Cookbook today!
In this article, we will look at some of the most prevalent causes of raised blood sugar levels in the absence of dietary sugar consumption, as well as various solutions to this problem.
- Carbohydrate Metabolism:
Carbohydrates are a key source of blood sugar (glucose) in the body. Even if you avoid sugary foods and drinks, your body can convert other types of carbs into glucose. During digestion, complex carbs such as bread, rice, pasta, and starchy vegetables are broken down into glucose, which might impact blood sugar levels.
Solution: Keep a close eye on your carbohydrate intake, emphasizing complex carbohydrates with a lower glycemic index. Balanced meals that include carbohydrates, fiber, protein, and healthy fats can help keep blood sugar levels stable.
- Stress and Hormones:
Physical or emotional stress can cause the release of stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. Even without consuming sugar, these hormones can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Furthermore, hormonal fluctuations associated with the menstrual cycle or other medical problems may have an impact on blood sugar management.
Solution: Use stress-reduction approaches such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and physical activity to successfully manage stress. If you suspect hormonal irregularities, get assessment and advice from a healthcare expert.
- Medications and Insulin:
Certain medications, including corticosteroids, some antipsychotics, and certain decongestants, can raise blood sugar levels. If you’re taking medications for other health conditions, be aware of their potential impact on glucose levels. Additionally, if you have diabetes and use insulin or other glucose-lowering medications, improper dosing or timing can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Solution: Consult your healthcare provider to review your medications and discuss potential alternatives or adjustments. If you have diabetes, work with your healthcare team to fine-tune your insulin or medication regimen.
- Dawn Phenomenon and Hormonal Fluctuations:
The dawn phenomenon, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels in the early morning hours, is a natural response to the body’s release of hormones like cortisol and glucagon. These hormones help prepare the body for the day ahead and can cause blood sugar levels to rise, regardless of dietary sugar intake.
Solution: To manage the dawn phenomenon, consider discussing medication adjustments or insulin timing with your healthcare provider. Regular physical activity and a balanced evening meal may also help stabilize morning blood sugar levels.
- Underlying Health Conditions:
Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), can affect insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. These conditions may lead to elevated blood sugar levels even without dietary sugar consumption.
Solution: If you suspect an underlying health condition, consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and appropriate treatment. Managing the underlying condition may help improve blood sugar control.
- Sleep Patterns and Quality:
Disrupted or inadequate sleep can impact blood sugar regulation. Poor sleep quality, irregular sleep patterns, and insufficient rest can lead to insulin resistance and higher blood sugar levels.
Solution: Prioritize good sleep hygiene by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques to improve sleep quality.
- Alcohol Consumption:
Alcohol can influence blood sugar levels, often causing them to drop initially and then rise later. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels the morning after consuming alcohol.
Solution: If you choose to consume alcohol, do so in moderation and be aware of its potential impact on your blood sugar levels. Monitor your glucose levels and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
High blood sugar levels while avoiding dietary sugar can be caused by a number of variables, including carbohydrate metabolism, stress, drugs, hormonal fluctuations, underlying health disorders, sleep habits, and alcohol intake. Working closely with your healthcare practitioner to discover the particular reason of your elevated blood sugar levels and build a personalized plan for controlling them effectively is critical. You can improve your blood sugar control and general health by addressing the underlying issues and making necessary lifestyle and medication changes.
Please Note: The diet and watching carbs DOES NOT fix the root issues that make blood sugar go up.