Understanding the Causes and Types of Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Causes and Types of Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. The condition is characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to a host of health problems, including heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney damage. There are several different types of diabetes, each with its own set of causes and risk factors. In this article, I’ll provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the causes and types of diabetes, including how they are diagnosed and treated in mainstream medicine. This comprehensive guide does not talk about reversing diabetes based on the results patients achieve in my office.
Understanding the Causes of Diabetes:
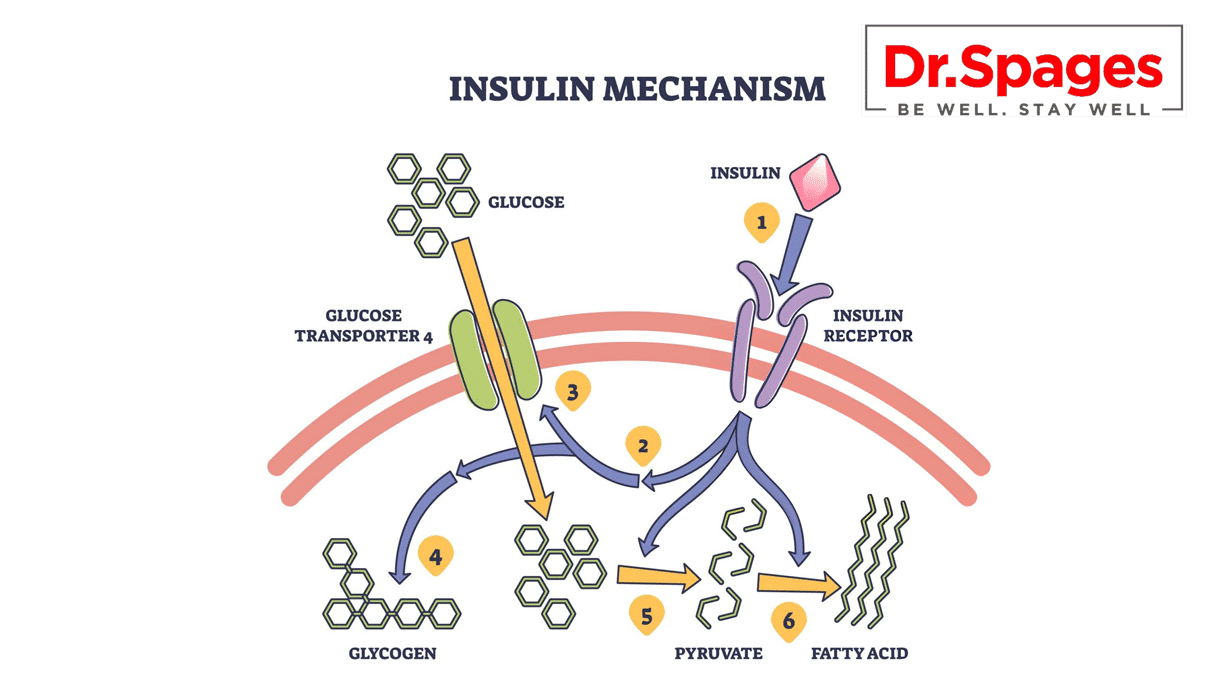
The underlying cause of diabetes is a lack of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas and many other factors which could raise sugar levels. When insulin is not produced or utilized properly, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. There are several different factors that can contribute to insulin dysfunction and the development of diabetes, including:
- Genetics: Diabetes can be inherited, and some genetic mutations may increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Lifestyle factors: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity can all increase the risk of developing diabetes.
- Age: The risk of developing diabetes increases with age, particularly after age 45.
- Infections: Diabetic tend to have underling chronic infections only seen with special testing.
- Adrenal problems: This includes imbalances with regulating cortisol the stress hormone of the body.
- Converting Hormones: Many diabetics convert hormones to the opposite sex due to inflammation and organ dysfunction.
- Liver Function: I have never seen in the last 20 years a type II diabetic with a “proper functioning liver”…ever. This is a reason why the metabolic clearing helps so many diabetics. It gets the liver functioning.
- Toxin Load: Many type II diabetics struggle with their body detoxing. Never mind the medication but also just the environmental toxins which can slow down healing.
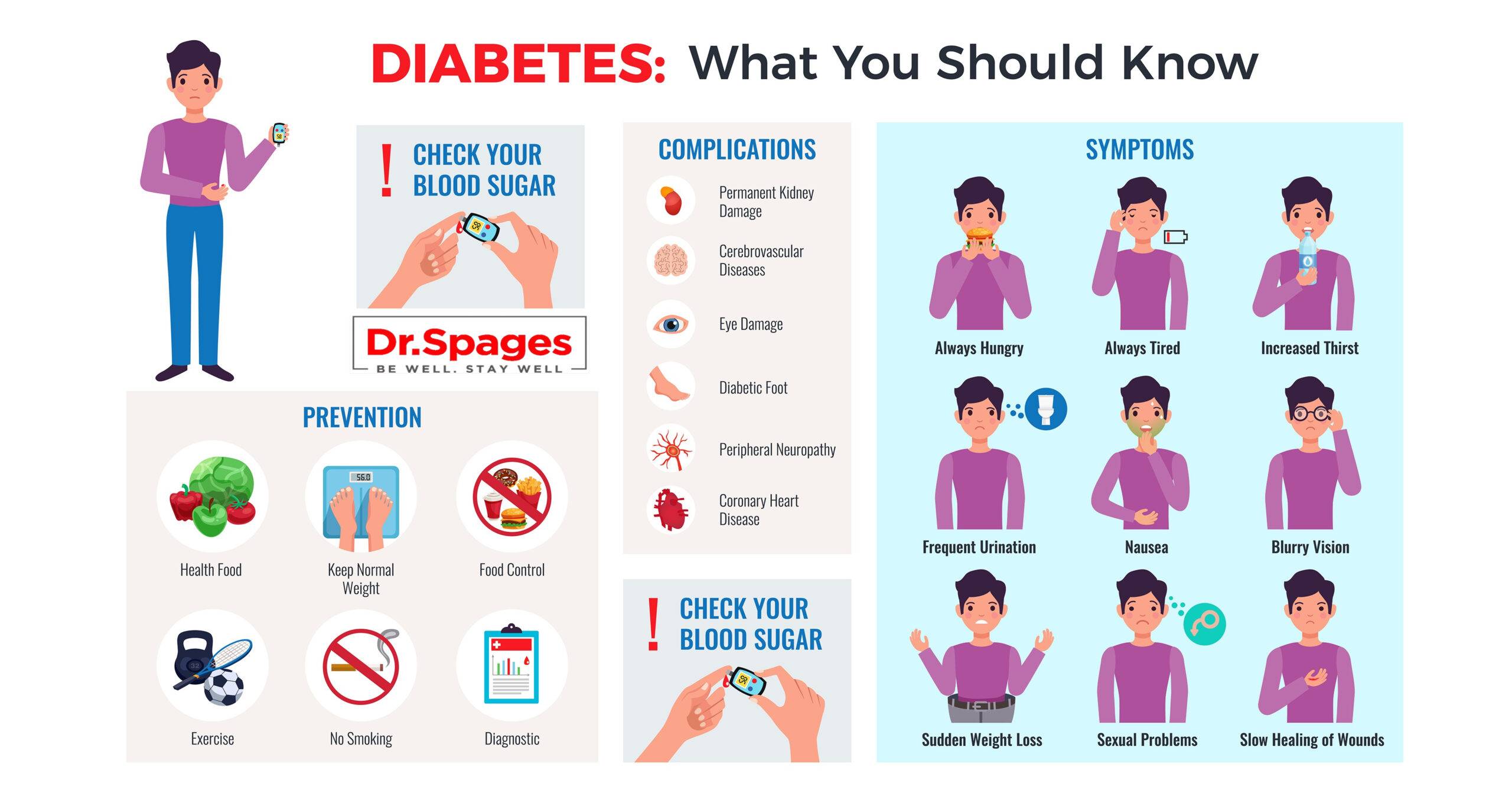
- Other health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can increase the risk of developing diabetes.
Types of Diabetes:
There are several different types of diabetes, each with its own set of causes and risk factors. Here are the most common types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks the pancreas, destroying the cells that produce insulin. This type of diabetes is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence and is not related to lifestyle factors.
- Type 2 diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes and is typically diagnosed in adulthood. It is often associated with lifestyle factors, including poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity. Type 2 diabetes can also be caused by genetics and other health conditions.
- Gestational diabetes: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and is typically diagnosed in the second or third trimester. It is caused by hormonal changes and insulin resistance associated with pregnancy and typically resolves after delivery.
- Prediabetes: Prediabetes is a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It is often a precursor to type 2 diabetes and can be managed through lifestyle changes.
- There are 1.5 diabetes which has an autoimmune component and also Type III Diabetes which include neurodegeneration.
Diagnosing Diabetes:
Diabetes is typically diagnosed through blood tests that measure fasting blood sugar levels above 126 or A1C levels over 6.5. Fasting blood sugar tests measure blood glucose levels after an overnight fast, while A1C tests measure average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. If blood sugar levels are consistently high, a diagnosis of diabetes may be made.
Treatment for Diabetes:
There are several different treatments available for diabetes, depending on the type and severity of the disease. These treat the symptom but DOES NOT FIX THE ROOT CAUSE. Here are some of the most common treatments for diabetes:
- Lifestyle changes: Making dietary changes, increasing physical activity, and losing weight can all help manage and even reverse prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
- Medication: Medications, including insulin, oral medications, and injectable medications, can help manage blood sugar levels in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
- Blood sugar monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring is critical for managing diabetes and preventing complications associated with high blood sugar levels.
- Surgery: Bariatric surgery may be an option for people with severe obesity and type 2 diabetes.
The treatment for diabetes is a step but does not address the causes of what makes someone unable to regulate their blood sugar on their own.
Conclusion:
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. The underlying cause should be determined in order to reverse it.
About Dr Spages
Dr. Jonathan Spages, DC is highly knowledgeable in Functional Medicine and has remarkable proficiency in treating the root causes of persistent illnesses, including type II diabetes and hypothyroidism. He has transcended the traditional methodology of using medications and hormones as the main therapy for these conditions. Instead, he employs state-of-the-art diagnostic testing and analytical methods to detect the underlying causes of these ailments, which are frequently disregarded in traditional medical practices.