Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Introduction
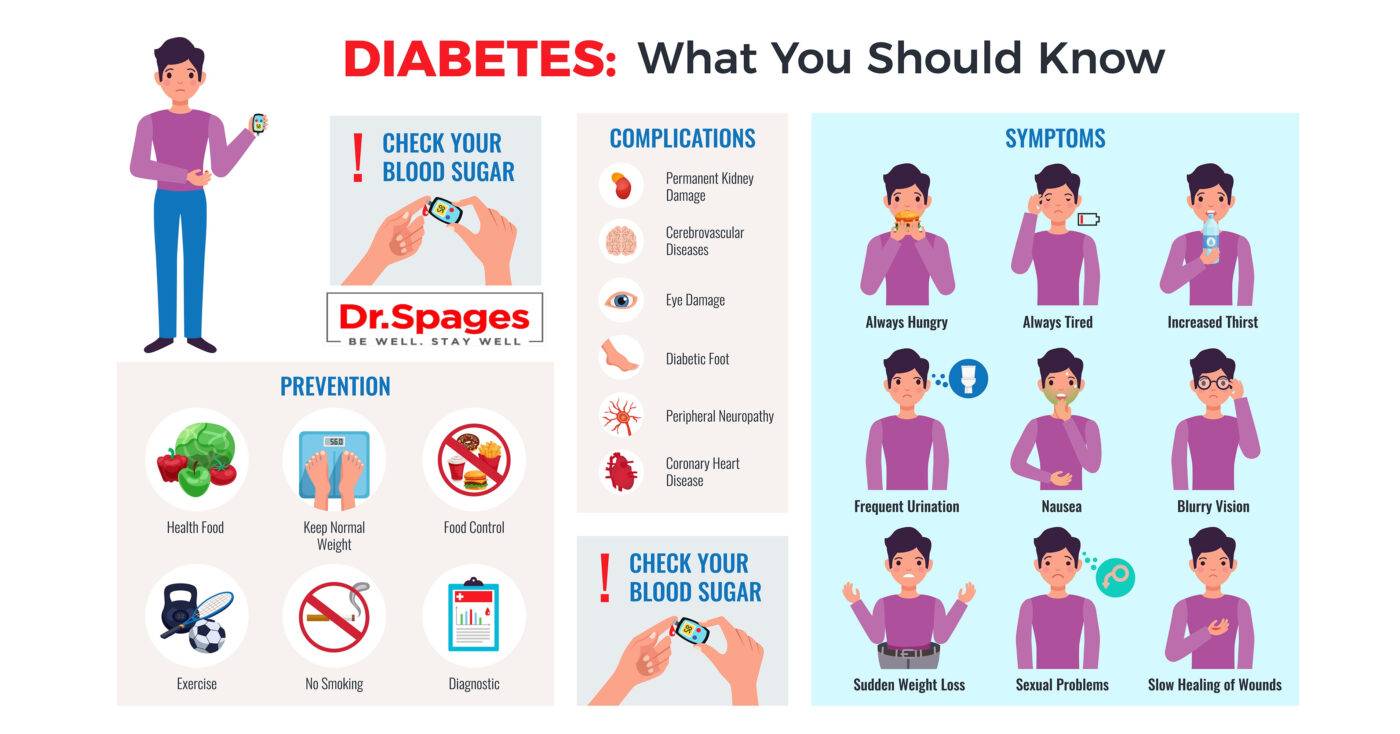
Diabetes, particularly type 2, presents a significant global health challenge, with prevalence continuing to rise. At the core of type 2 diabetes lies insulin resistance—a metabolic dysfunction where cells exhibit reduced responsiveness to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. In this article, I’ll delve into the root causes of insulin resistance, its intricate relationship with type 2 diabetes, and how addressing these causes can pave the way for reversing the condition. We will also explore the diagnostic tools, preventive measures, and sustainable lifestyle changes critical for achieving long-term success.
Root Causes of Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
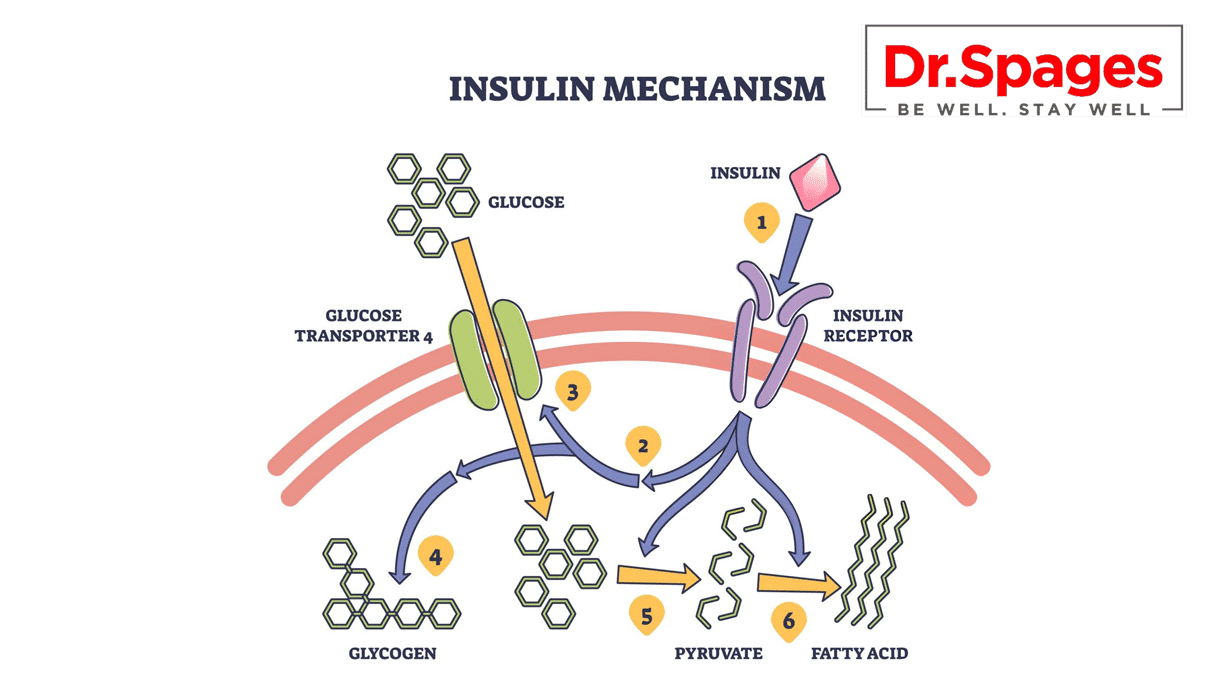
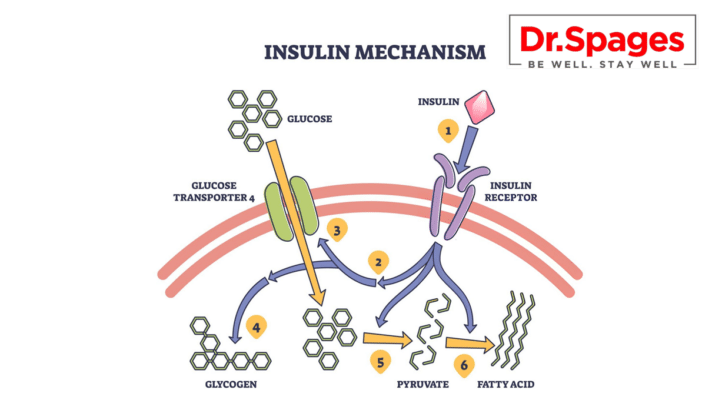
Insulin, a vital hormone produced by the pancreas, regulates blood sugar by facilitating glucose uptake into cells for energy or storage. In individuals with insulin resistance, cells fail to respond effectively to insulin signals, leading to glucose buildup in the bloodstream. To compensate, the pancreas increases insulin production, resulting in hyperinsulinemia. Over time, this overcompensation can fail, leading to sustained high blood sugar levels—characteristic of type 2 diabetes.
Rather than addressing symptoms, it is crucial to uncover and target the underlying causes of insulin resistance.
These include:
1. Chronic Inflammation and Gut Health: Systemic inflammation, often driven by poor dietary choices and gut dysfunction, disrupts insulin signaling. Gluten and grains are common culprits that exacerbate this inflammation and impair gut integrity, compounding insulin resistance.
2. Organ Dysfunction: Compromised liver and pancreas function significantly impact glucose metabolism and insulin production. Restoring these organs’ health is essential for reversing diabetes.
3. Lifestyle Factors: Sedentary behavior, poor sleep quality, chronic stress, and imbalanced diets worsen insulin sensitivity and exacerbate the condition. This is seen in adrenal saliva testing I examine on patients.
4. Excessive Exercise: Interestingly, intense or prolonged exercise can sometimes increase insulin resistance, especially if the body is already under significant stress or inflammation.
Mechanisms Behind Insulin Resistance
At a cellular level, insulin resistance stems from disruptions in insulin signaling pathways, often exacerbated by:
Chronic low-grade inflammation: Pro-inflammatory cytokines interfere with insulin receptor function, reducing glucose uptake.
Oxidative stress: An imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants impairs insulin signaling.
Genetic predispositions: Variations in insulin-related genes (e.g., IRS-1 and TCF7L2) may influence sensitivity and risk.
A Root-Cause Approach: Gluten-Free and Grain-Free Diet
Addressing the root cause of insulin resistance starts with eliminating gluten and grains, which contribute to systemic inflammation, disrupt gut health, and impair organ function. By adopting a gluten-free and grain-free diet, individuals can reduce inflammation, support gut integrity, and optimize liver and pancreas health—paving the way for reversing insulin resistance.
Key Strategies for Preventing and Reversing Type 2 Diabetes
1. Dietary Changes:
Adopt a gluten-free, no grains diet to reduce inflammation and restore gut and metabolic health.
Balance blood sugar with low-glycemic index foods, fiber-rich vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Support organ health with nutrient-dense foods like leafy greens, bitter melon, cinnamon, and fenugreek.
2. Exercise with Caution:
Engage in moderate-intensity activities like walking, swimming, or yoga. Over-exercising or high-intensity workouts can increase inflammation and worsen insulin resistance in some cases. Finding a balance is key.
3. Stress Management:
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, exacerbating insulin resistance. Mindfulness, deep breathing, and relaxation techniques can significantly improve metabolic balance.
4. Prioritize Sleep:
Poor sleep disrupts hormone regulation and metabolism. To support insulin sensitivity, aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night.
5. Functional Medicine Approach:
A functional medicine perspective focuses on uncovering the unique root causes of each individual’s insulin resistance. To facilitate reversal, personalized treatment plans can address specific dietary, lifestyle, and genetic factors.
Diagnostic Tools for Insulin Resistance
Accurate diagnosis is essential for tailoring interventions. Tools include:
Fasting insulin and glucose levels.
Oral glucose tolerance tests.
HOMA-IR calculations to measure insulin resistance.
Comprehensive assessments of lifestyle, inflammation markers, and organ function.
Conclusion
Insulin resistance, a key driver of type 2 diabetes, arises from a complex interplay of dietary, lifestyle, and genetic factors. Addressing the root causes—such as systemic inflammation, gut dysfunction, and organ health—offers a transformative path to reversing this condition. Adopting a gluten-free, grain-free diet, balancing physical activity, managing stress, and improving sleep quality are crucial components of this holistic approach.
Reversing type 2 diabetes is not just about managing blood sugar but uncovering and resolving the metabolic imbalances that fuel the condition. By empowering individuals with knowledge and actionable steps, we can move beyond symptom management to achieving long-term health and vitality. For those seeking deeper guidance, this free course on reversing diabetes offers a roadmap to reclaiming optimal health and well-being.
If you’re based in Florida and are ready to take the first step toward reversing diabetes, I’d love to help! Don’t hesitate to fill out this application form for a consultation tailored to your needs. Let’s work together to reclaim your health!
Suggested Resources:
References
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/insulin-resistance.html
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3314346/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22206-insulin-resistance












I have type one diabetes, taking medforman and lisinopril